Hledej
Zobraz:
Univerzity
Kategorie
Rozšířené vyhledávání
12 662
projektů
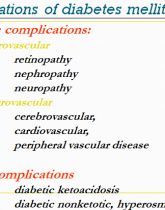
Complications of Diabetes Mellitus
| Přípona .ppt |
Typ prezentace |
Stažené 0 x |
| Velikost 2,9 MB |
Jazyk anglický |
ID projektu 5615 |
| Poslední úprava 20.04.2015 |
Zobrazeno 1 638 x |
Autor: stefan.potocky |
 Sdílej na Facebooku
Sdílej na Facebooku |
||
| Detaily projektu | ||
- Cena:
2 Kreditů - kvalita:
88,2% -
Stáhni
- Přidej na srovnání
- Univerzita:Veterinární a farmaceutická univerzita Brno
- Fakulta:Farmaceutická fakulta
- Kategorie:Přírodní vědy » Zdravotnictví, lékařství
- Předmět:Farmakologie
- Studijní obor:Farmakologie
- Ročník:3. ročník
- Formát:MS Office PowerPoint (.ppt)
- Rozsah A4:31 stran
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Insulin deficiency causes wasting through increased breakdown and reduced synthesis of proteins. Diabetic ketoacidosis is an acute emergency. It develops in the absence of insulin because of accelerated breakdown of fat to acetyl-CoA, which, in the absence of aerobic carbohydrate metabolism, is converted to acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate (which cause acidosis) and acetone (a ketone).
diabetic nonketotic, hyperosmolar coma
Microvascular complications are specific to diabetes and do not occur without longstanding hyperglycaemia.
Other metabolic, environmental and genetic factors are undoubtedly involved in their pathogenesis.
Both T1DM and T2DM are susceptible to microvascular complications, although patients with T2DM are older at presentation and may die of macrovascular disease before microvascular disease is advanced.
Diabetic nephropathy affects 20-40% of patients with T1DM, particularly those presenting before puberty and possibly those with an inherited tendency to hypertension.
T2DM patients are also susceptible to nephropathy.
Over 40% of subjects with T1DM survive more than 40 years, half of them without developing significant micro-vascular complications.
Insulin deficiency causes wasting through increased breakdown and reduced synthesis of proteins. Diabetic ketoacidosis is an acute emergency. It develops in the absence of insulin because of accelerated breakdown of fat to acetyl-CoA, which, in the absence of aerobic carbohydrate metabolism, is converted to acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate (which cause acidosis) and acetone (a ketone).
diabetic nonketotic, hyperosmolar coma
Microvascular complications are specific to diabetes and do not occur without longstanding hyperglycaemia.
Other metabolic, environmental and genetic factors are undoubtedly involved in their pathogenesis.
Both T1DM and T2DM are susceptible to microvascular complications, although patients with T2DM are older at presentation and may die of macrovascular disease before microvascular disease is advanced.
Diabetic nephropathy affects 20-40% of patients with T1DM, particularly those presenting before puberty and possibly those with an inherited tendency to hypertension.
T2DM patients are also susceptible to nephropathy.
Over 40% of subjects with T1DM survive more than 40 years, half of them without developing significant micro-vascular complications.
Klíčová slova:
Complications
Cardivascular
Insulin
Proteins
Emergency
Metabolism
Diabetes
Patients
Subject
Pathophysiology
Disease
Plasma
Glucose
Damage
Nerve
Lens
Retina
Enzyme
Accumulation
Obsah:
- Complications of diabetes mellitus
Acute complications
Chronic complications
Microvascular complications
Pathophysiology of microvascular disease
Diabetic retinopathy. Laser photocoagulation.
1. Diabetic nephropathy.
Macrovascular Effects
Heart attack
Diabetic foot